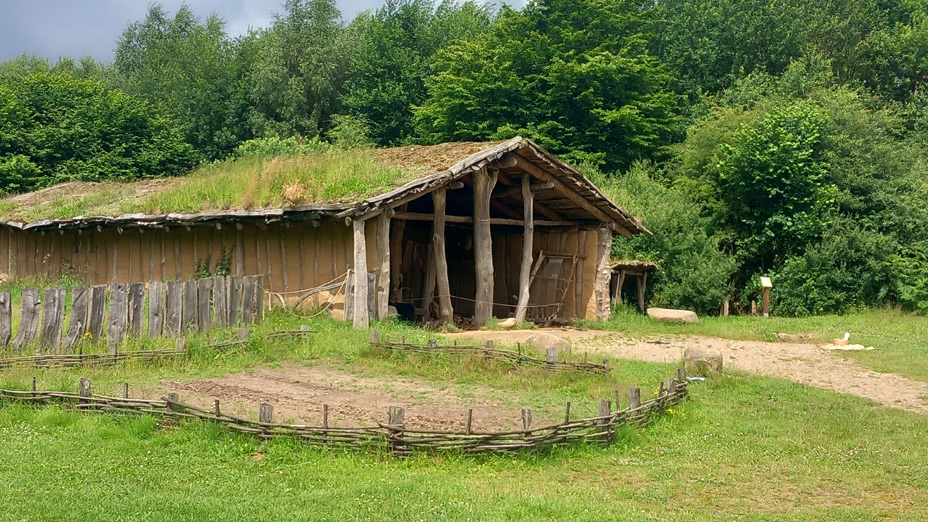
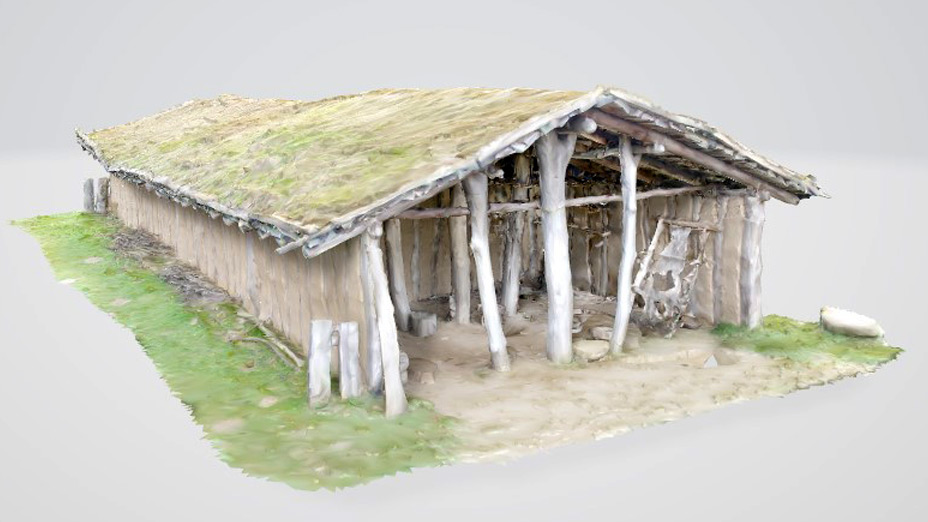
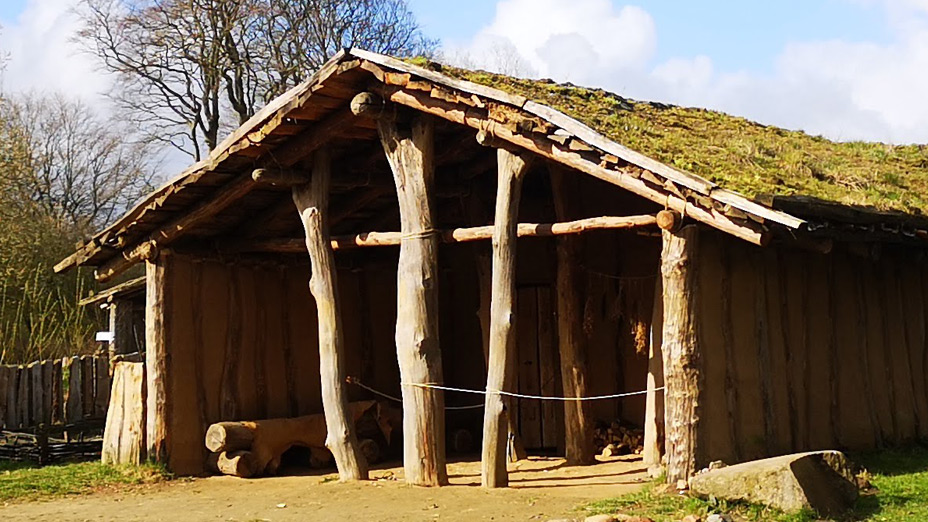
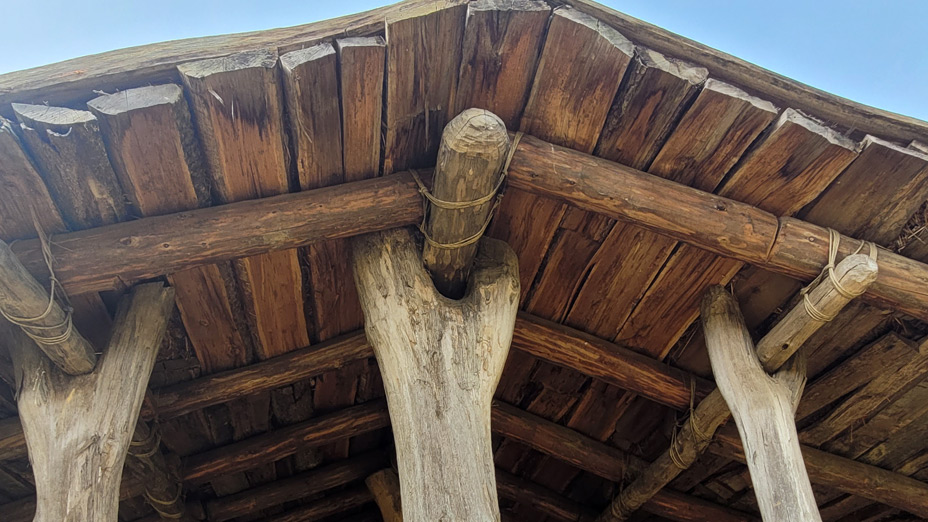
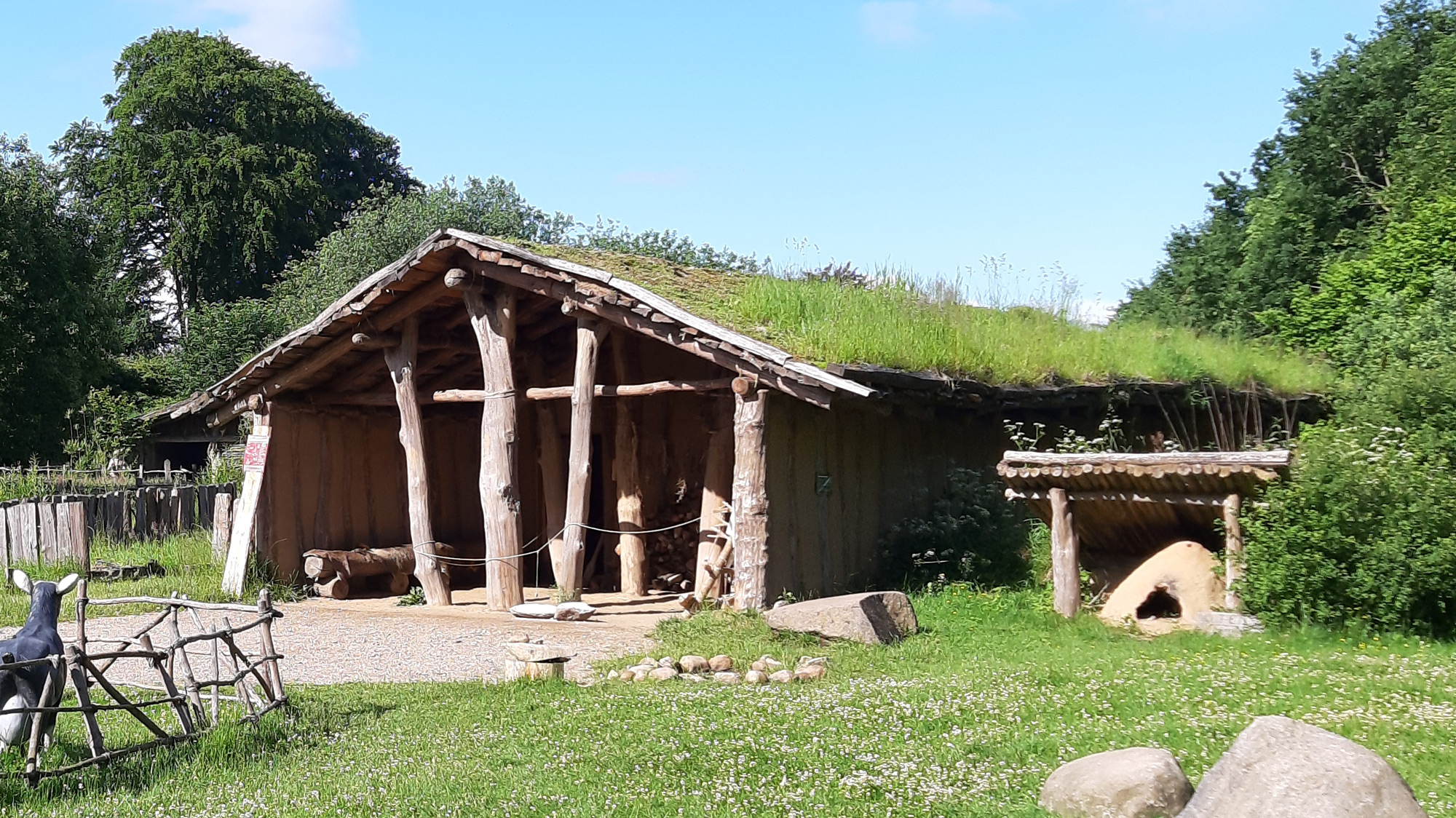
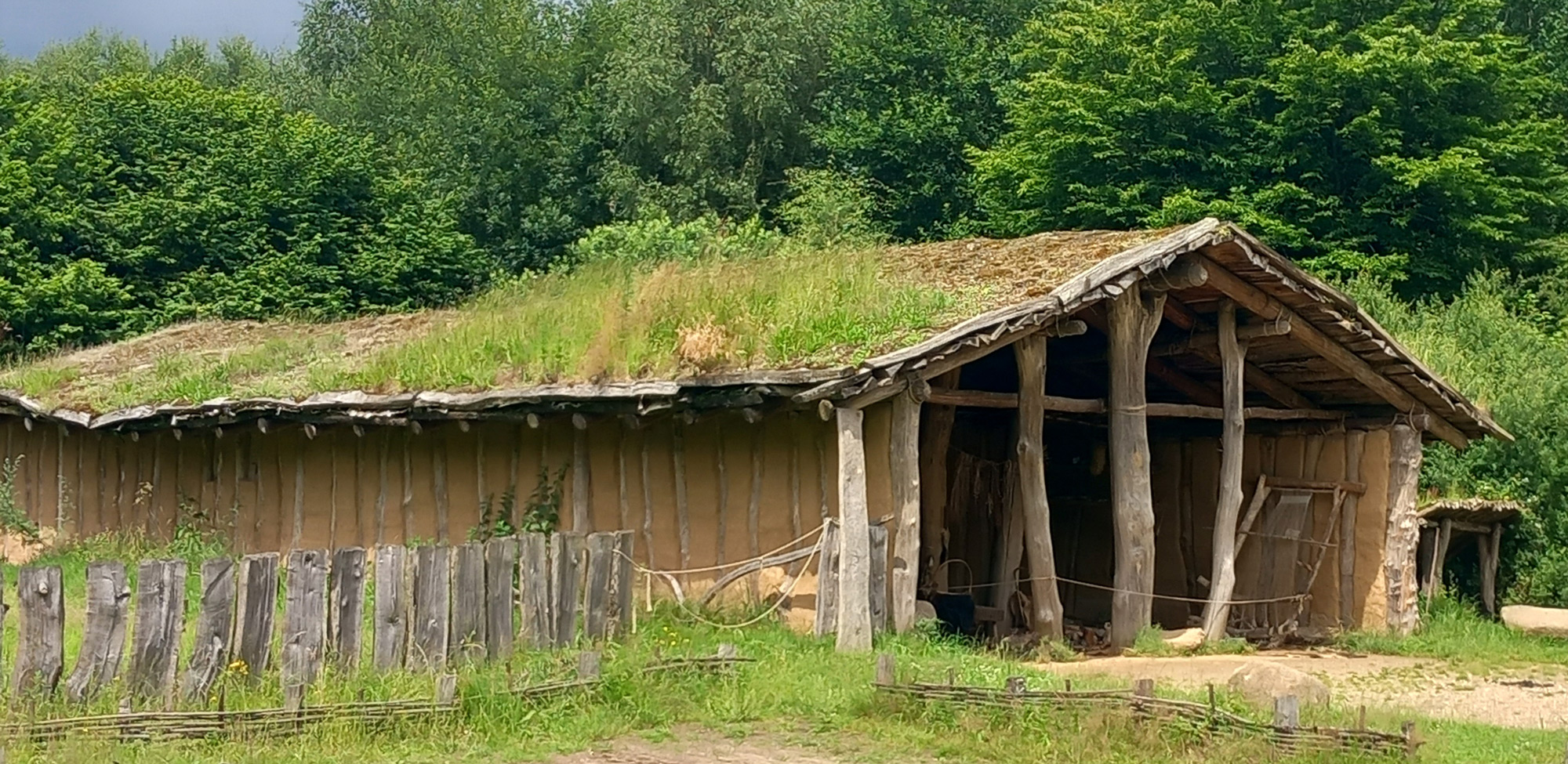
Stone Age House of Pennigbüttel
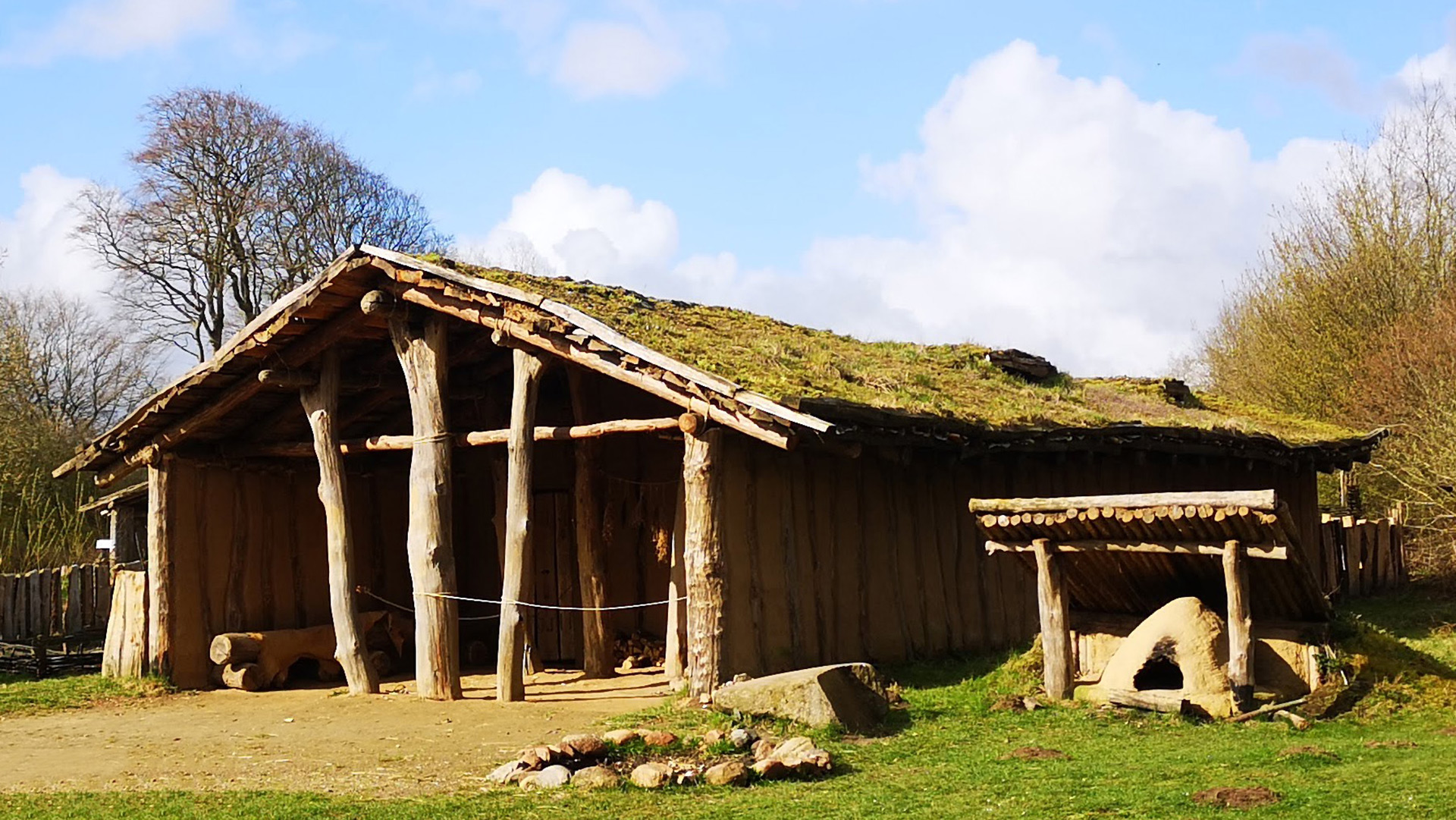

Name of the building in the museum in English: Stone Age House of Pennigbüttel
Name of the building in local language (as used in the museum): Steinzeithaus Pennigbüttel
Local Language: German
Type of building:
Reconstruction (a new building, based on either historical or archaeological sources but without using original substance)
Museum where the building is presently located:
Steinzeitpark Dithmarschen (DE)
Please select extra information below:
The original building or its remains: Source and Inhabitants
Source Material
Name of the location: Pennigbüttel | See Google Map below
Address: Siemensstraße | Osterholz-Scharmbeck - Pennigbüttel. D - 27711 | Germany
Organisation responsible for in situ excavation:
Bezirksarchäologie Lüneburg | Germany | Website
Name of the person responsible for the excavation: Jan J. Assendorp
Role of the person documenting: Archaeologist
When the excavation took place: 1985-1986
Source(s): Relevant academic literature (3.4 MB) | Plan of the excavation
Jan J. Assendorp, 2000, Die Bauart der trichterbecherzeitlichen Gebäude von Pennigbüttel, Niedersachsen. In: R. Kelm (ed.), Vom Pfostenloch zum Steinzeithaus. Archäologische Forschung und Rekonstruktion jungsteinzeitlicher Haus- und Siedlungsbefunde im nordwestlichen Mitteleuropa. Albersdorfer Forschungen zur Archäologie und Umweltgeschichte, Bd. 1. Heide. P. 116 – 125.
53.219318, 8.796069
Time and Inhabitants
The historical /archaeological time period of the original building is:
Neolithic
The original building date / date of first construction of the building is:
3200 BC
Cultural group is known as:
Funnel Beaker Culture
Is the information about the original building's owners / users / inhabitants known?
No
About the original building
The original building was:
Part of a settlement
If part of a settlement, what is the original building's environment:
Household / homestead
What was the name of the household?
Unknown
What was the location of the original building within the household?
Unknown
The original function of the (original) building was:
Residential
If the original building was residential, the primary type was:
Farmhouse
Has the building's function of use changed through its history?
No
The building in the museum: Basic facts and Construction process
The importance
The reason to present this building in the museum is:
The building is a rare specimen of its type, The building is a prime example of the architectural characteristics, The building is of technological interest
Please explain the rarity:
There are only a very few findings and excavations of neolithic houses in Northern Germany.
Please explain the unique architectural characteristics:
The building with three roof bearing posts is very characteristic (and it allows very high weights, like here for grass sods on the roof).
Please explain the specific technological interest:
The building technique with three bearing posts and a roof made out of grass sods.
The reconstructed building was build on the site of the archaeological feature:
No
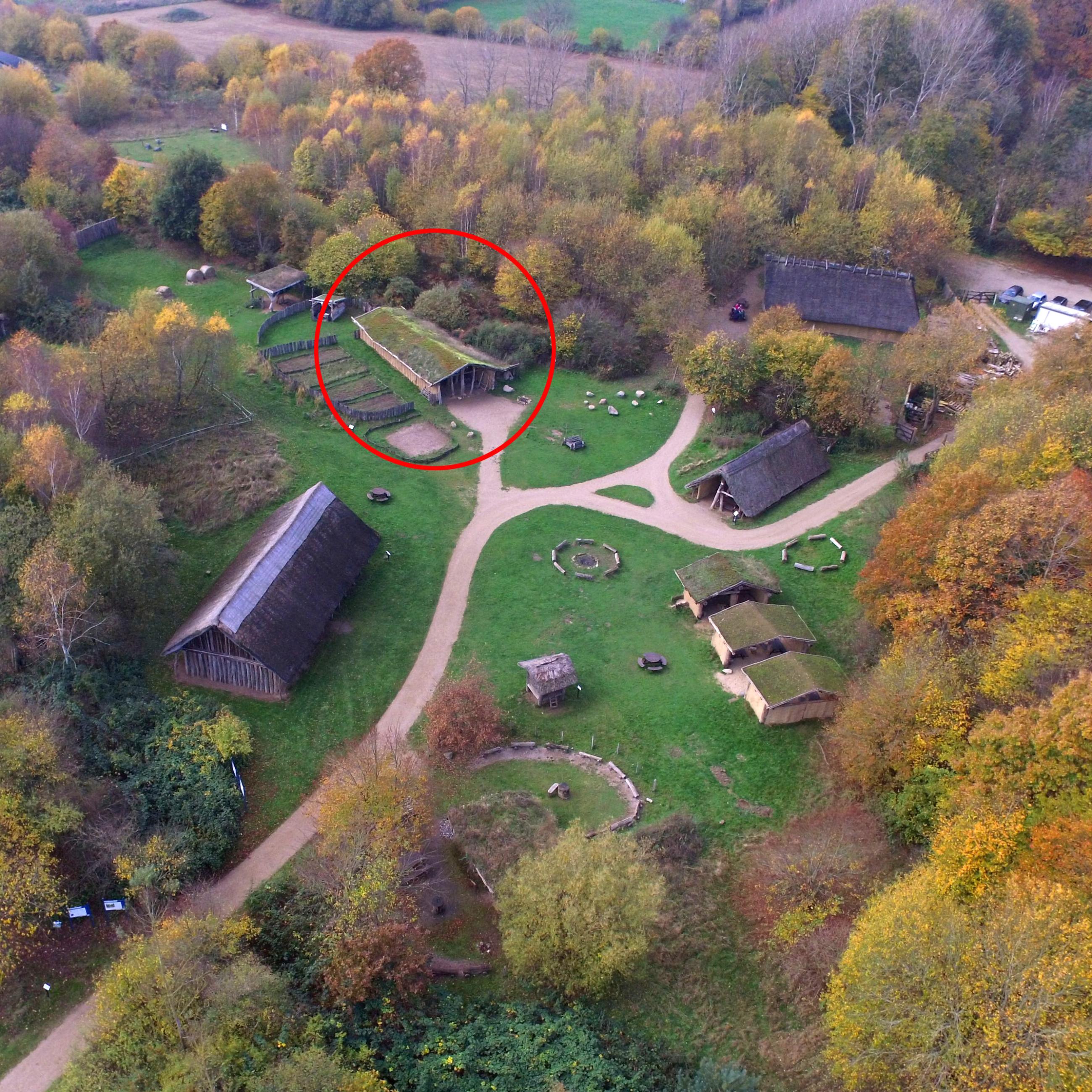

The location in the museum
Registration number / name / inventory number of the building: Neo 2
Location in the museum: In the area of the neolithic village (open-air area)
The building in the museum is: Part of a household
The household is: A reconstruction of the original household
The name given to the household by the museum is: "House of Pennigbüttel " (A and B)
The current location of the building within the household is: In the neolithic village area

Documentation of the Construction Process
Is the organisation constructing / rebuilding the building in the museum a RETOLD partner:
Yes
Name of the organisation conducting the construction / rebuilding:
Steinzeitpark Dithmarschen (DE)
Name of the person responsible for construction:
Volker Heesch
Role of the person within the organisation:
Leader of the working group (presently retired)
Process 1: Theoretical-scientific discussion about the construction of the house and its elements (Relevant academic literature, 3.4 MB)
Source: Birte Meller, 2005, Von Grundbedürfnis und mutmasslicher Notwendigkeit. Möglichkeiten der Innenraumgestaltung archäologischer Hausrekonstruktionen. In: R. Kelm (ed.), Frühe Kulturlandschaften in Europa. Forschung, Erhaltung und Nutzung. Albersdorfer Forschungen zur Archäologie und Umweltgeschichte, Bd. 3. Heide. P. 140 – 149.
Process 2: (Re)Construction of the interior a of Neolithic House (Relevant academic literature, 4.01 MB)
Source: Jan J. Assendorp, 2000, Die Bauart der trichterbecherzeitlichen Gebäude von Pennigbüttel, Niedersachsen. In: R. Kelm (ed.), Vom Pfostenloch zum Steinzeithaus. Archäologische Forschung und Rekonstruktion jungsteinzeitlicher Haus- und Siedlungsbefunde im nordwestlichen Mitteleuropa. Albersdorfer Forschungen zur Archäologie und Umweltgeschichte, Bd. 1. Heide. P. 116 – 125.
Process 3: Reconstruction of the Pennigbüttel House (Relevant academic literature, 7.96 MB)
Source: Frank M. Andraschko et al., 2005, Modellbau jungsteinzeitlicher Häuaser aus Norddeutschland im Archäologisch-Ökologischen Zentrum Albersdorf – Rekonstruktive Grundlage, Erfahrungen und Probleme aus der Praxis. In: R. Kelm (ed.), Frühe Kulturlandschaftne in Europa. Forschung, Erhaltung und Nutzung. Albersdorfer Forschungen zur Archäologie und Umweltgeschichte, Bd. 3. Heide. P. 119 – 139.
Significant diversion
Is there a significant diversion in the construction from the original:
Yes
Please provide reasons for the changes:
Safety reasons, costs, durability
Are materials, techniques or tools diverging from historical/archaeological accuracy?
Yes
Please provide reasons for the changes:
Safety reasons, costs durability
The building in the museum: Detailed Technical Description
General Information
Does the building have more than one floor? No
Floorplan ground floor: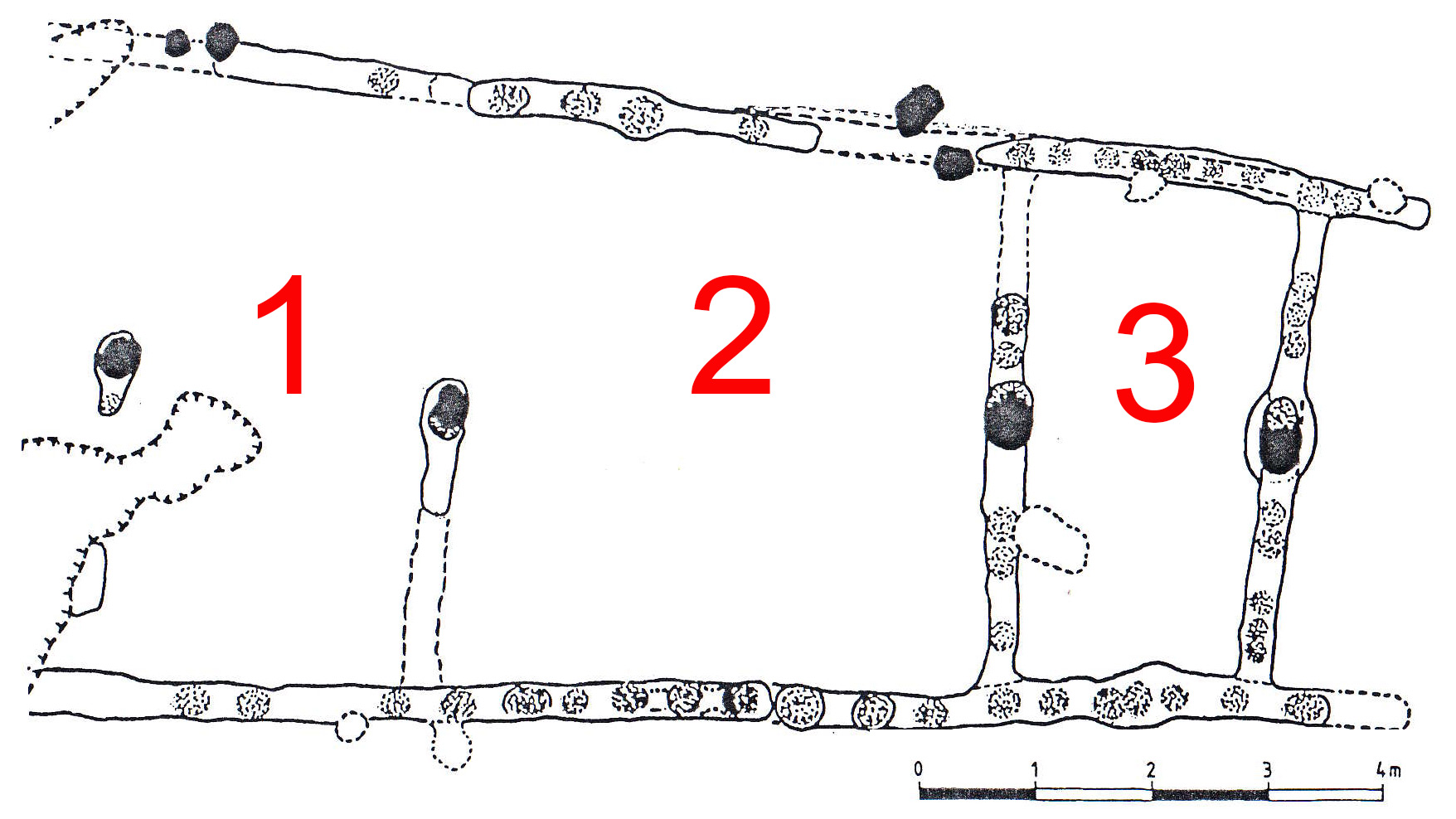 Room(s)
Room(s)
Room 1
Name of the room: Entrance Hall for working and cooking
Dimensions of the room: Height: 4000 mm | Width: 5500 mm | Depth: 3500 mm
Please select the relevant floor / level: Ground floor
Room 2
Name of the room: Main room for living and working
Dimensions of the room: Height: 4000 mm | Width: 5200 mm | Depth: 5000 mm
Please select the relevant floor / level: Ground floor
Room 3
Name of the room: Storage room
Dimensions of the room: Height: 4000 mm | Width: 4800 mm | Depth: 2800 mm
Please select the relevant floor / level: Ground floor
View(s) and Cross section(s):
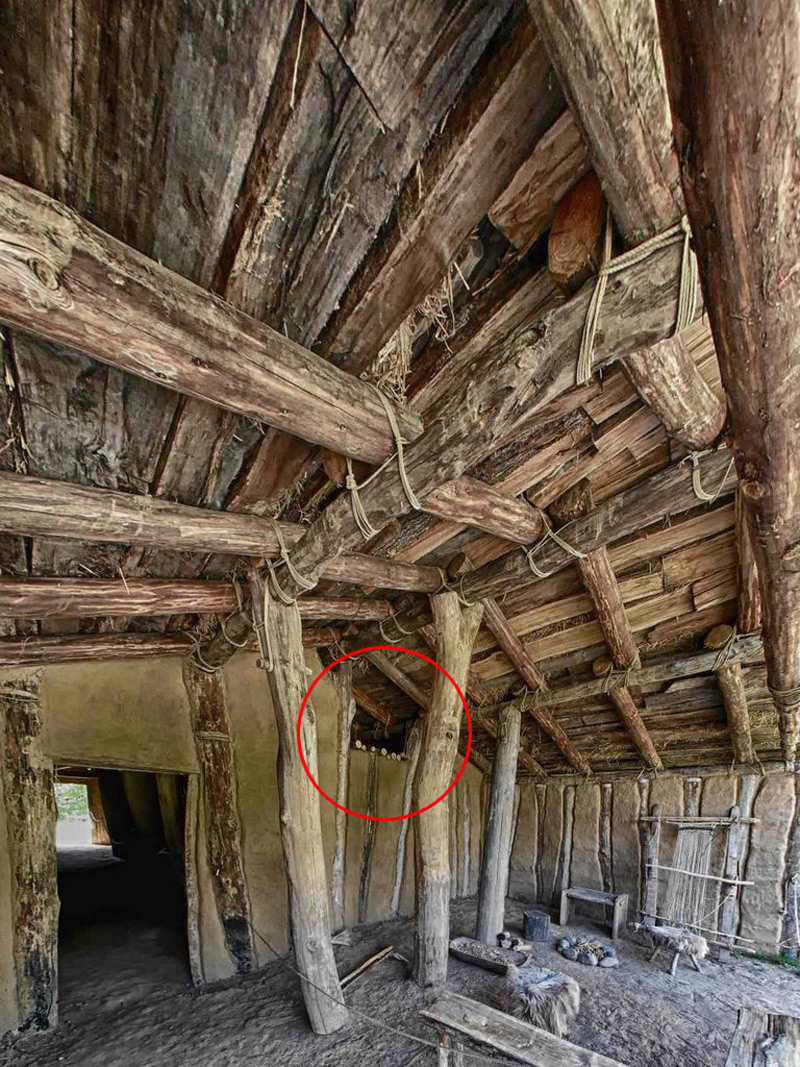
The load bearing elements and frame construction
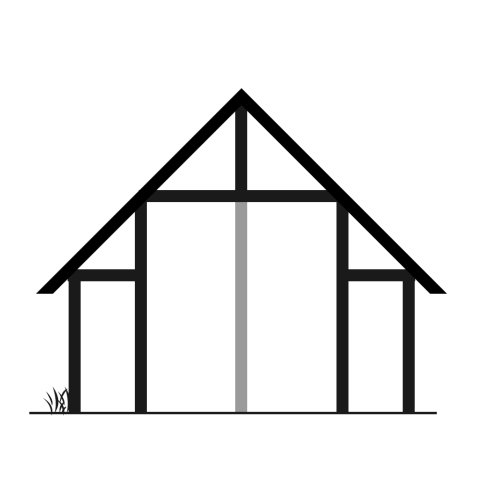
Please select the model which represents the construction of the building in the museum best: Model 5
Please describe the construction:
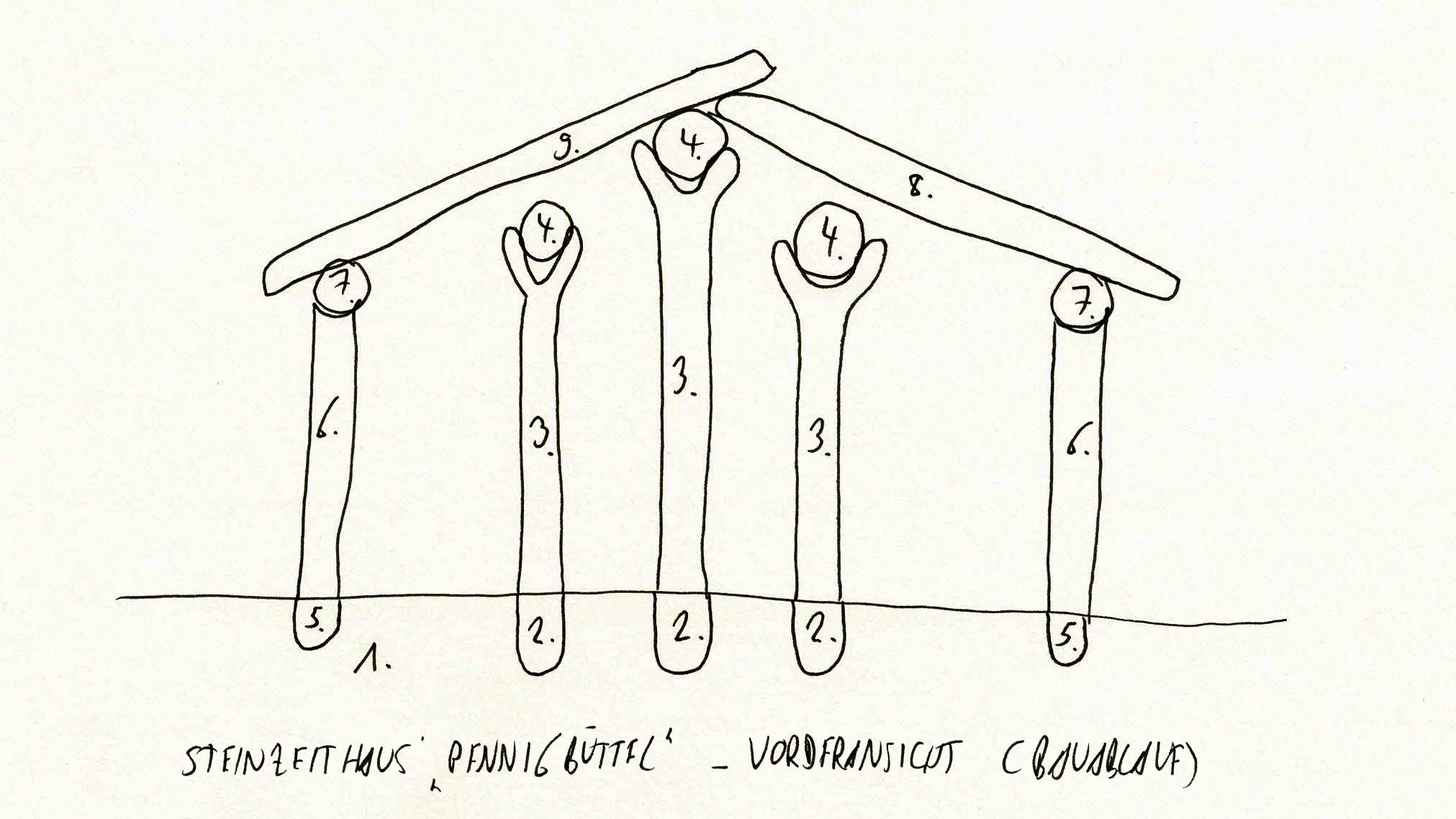
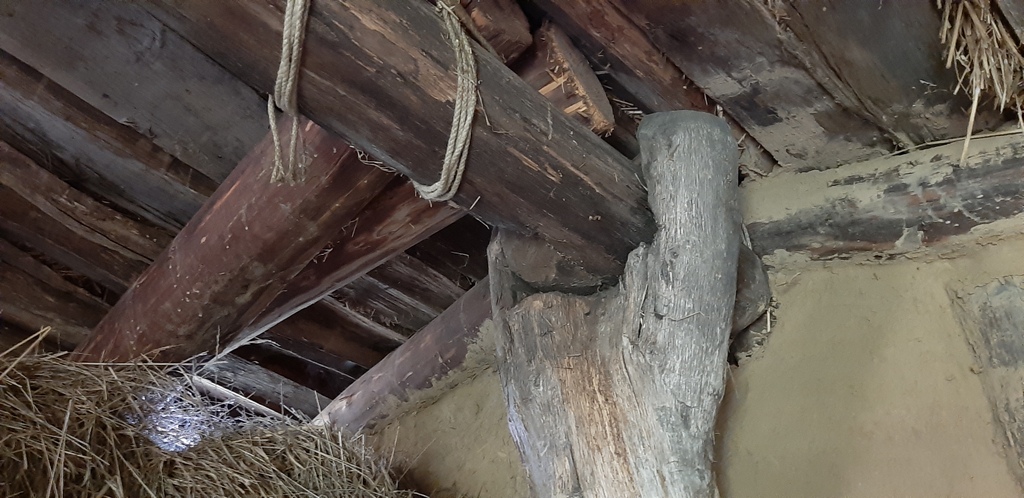
The dimension of the house is: L 1250 mm x B max. 5500 mm (min 4500 mm) x H 4000 mm. The ground plan of the house is trapezoidal. The construction has three roof bearing posts (which led to the reconstruction with a heavy grass sod roof).
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The construction has a duration of about 15 - 25 years. We built the first house structure in 1999 and repaired it totally in 2019.
Construction element
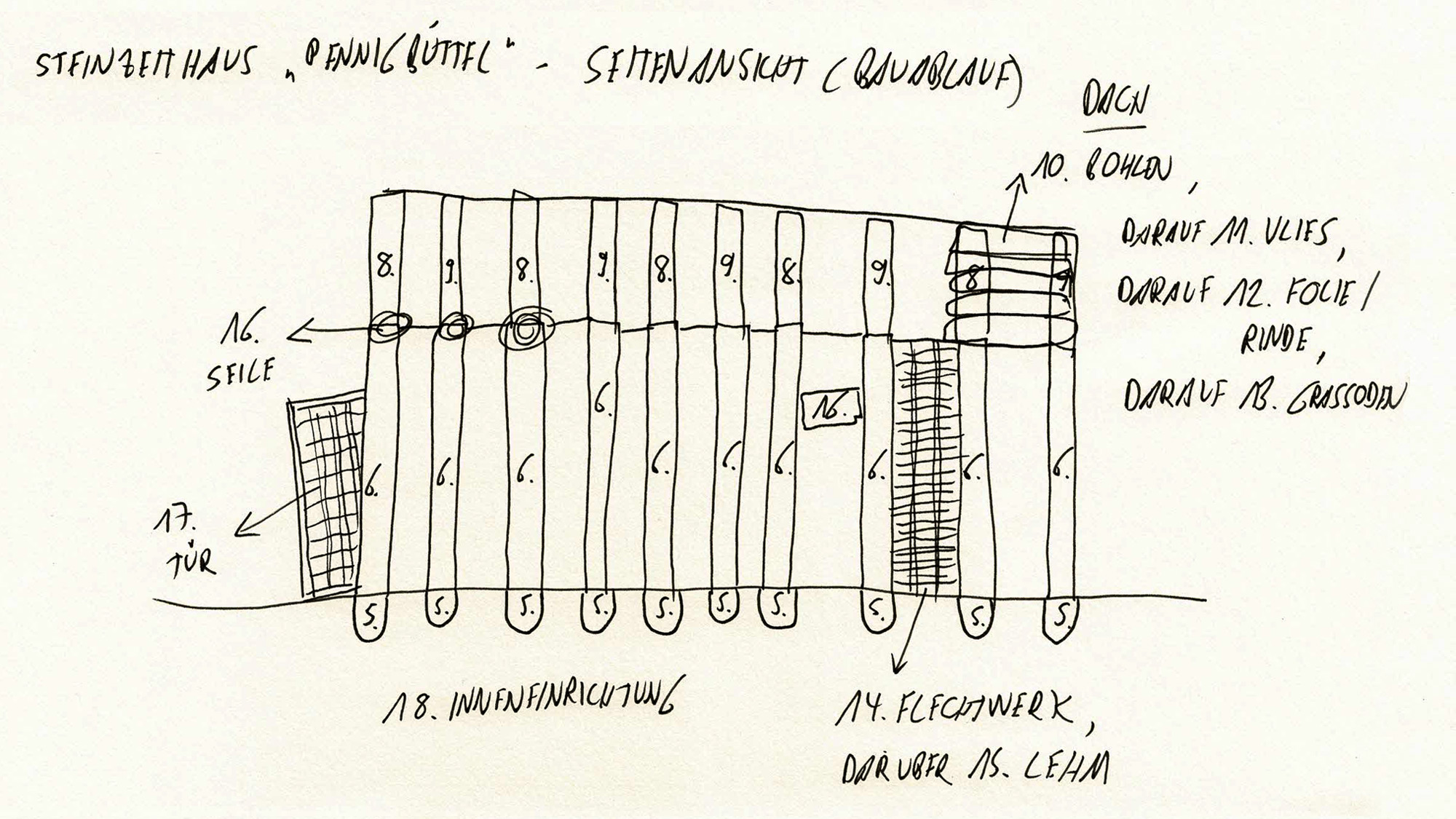
Name of the construction element: Building wood / posts and splitted wood. There are 12 bearing posts and 84 smaller posts for the wattle walls.
Material: timber - wood
Extra information about the selected material, its quality and finish: Big posts made of durable / resistant / hard oak tree, different sizes
Manufacturing technique: Preparing the posts with (flint) axes
Dimensions: The posts have a size of min. 2500 mm length (height) x 150 mm diameter (for the wattle wall posts) and max. 5000 mm length (height) x 600 mm diameter (for the roof bearing posts).
The groundwork/foundation (below ground)
Depth below ground: 500-800 mm
Select material: timber - wood
Additional information about the selected material:
In the ground you find around 100 posts, max. in a depth of 800 mm, min. in a depth of 500 mm.
Manufacturing techniques:
The posts have been felled in the forest, the bark has been removed and the posts have been placed in dug out post holes in the soil.
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The status of the posts in the soil is stabile after more than 15 years of use, also if the outer / smoother parts of the posts have been rotten (the hard inner part of the posts still guarantees stability of the construction).
The groundwork/foundation (above ground)
Select material: timber - wood, mud - clay - sand
Additional information about the selected material:
The groundwork consists of posts, wattle and clay walls. Here you find in a distance of every 30 cm a new post, where the space inbetween the posts has benn filled with small wattle and clay walls.
Manufacturing techniques:
The open spaces between the posts in the wall have a size of min. 15 cm and of max. 35 cm; this open spaces have been filled and structured by wattle walls inbetween. As last step the wattle walls have been structured with clay (prepared with sand, straw and cow dung), which coverst he wattle wall construction oft he whole house.
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The wattle walls with clay have to be repaired every second year (mostly by filling the existing gaps in the wall with prepared clay); the posts are not rotten, but stabile.
Wall type (primary)
Material(s): Wooden logs, Wattle and daub
Manufacturing techniques:
Erecting at first the Wooden logs and then build the wattle walls
Wall connection type: The wattle construction connects the logs
Corner joint type: rectangular (with posts in the corner)
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The clay / wattle walls have to be renewed every two years
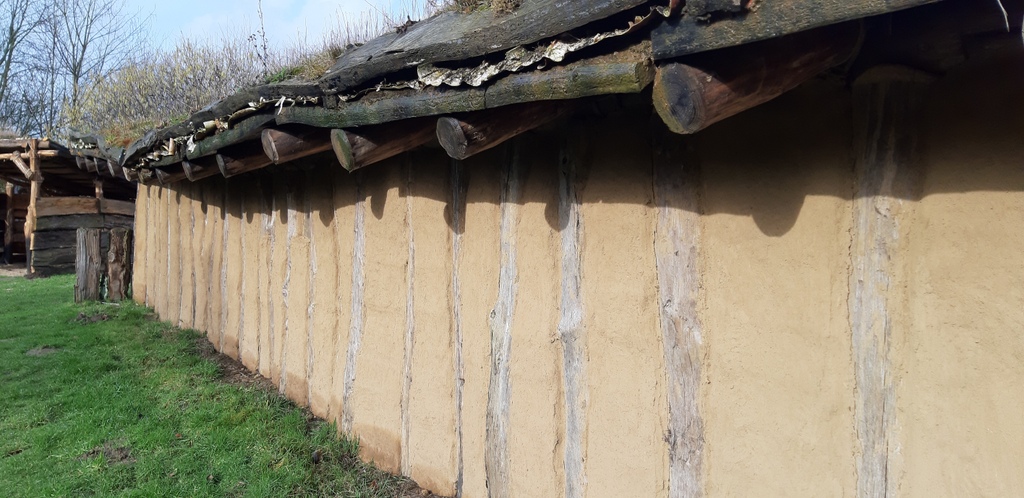
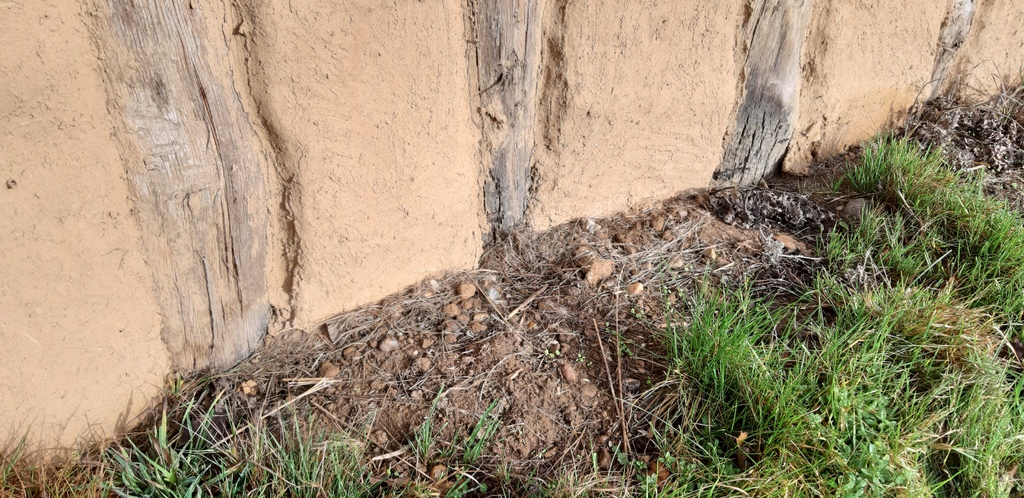


The details of the floors and ceilings - Ground floor
Flooring Type: Clay floor
Select material: mud - clay - sand
Additional information about the selected material:
The clay have to be tempered (with sand, straw and cow dung)
Manufacturing techniques:
Construct the clay floor by hand, and make it an even ground with a wooden plank
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The clay have to be renewed every second year
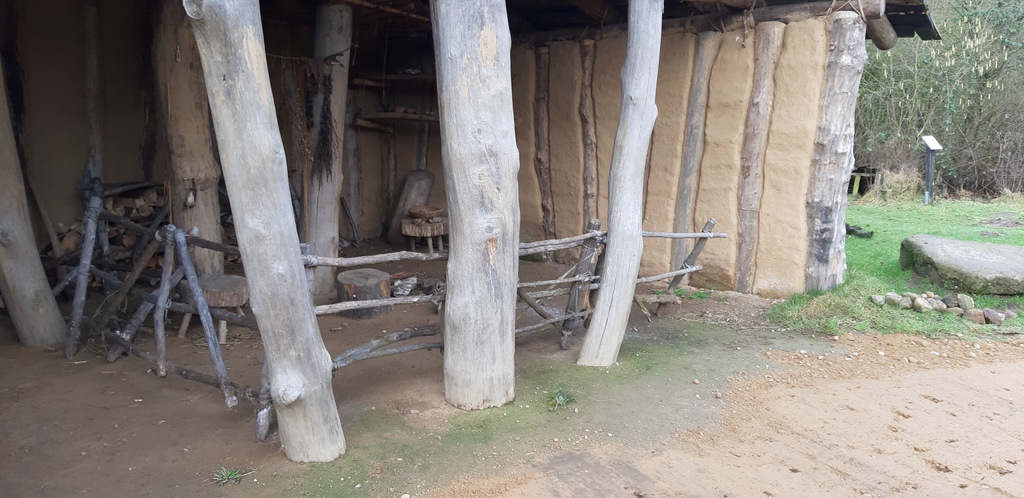

Roof structure
Select the model which represents the type of the roof best: Gable roof
Select the model which represents the frame type of the roof best: Common
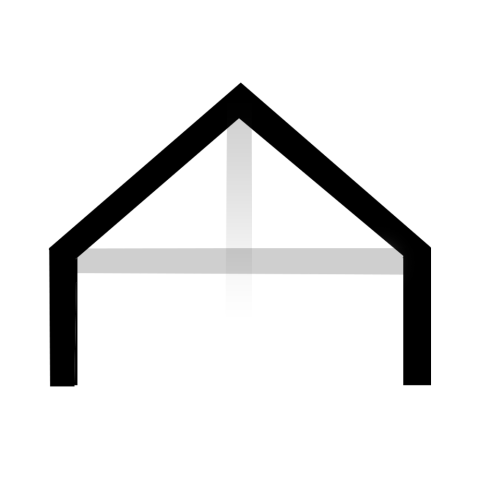

Select the material used to make the structure of the roof:
timber - wood
Additional information about the selected material:
oak tree
Manufacturing technique:
Prepare the oak wood planks
Frame height: 4000 mm
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The wood have to be checked every year, also if there are any static problems
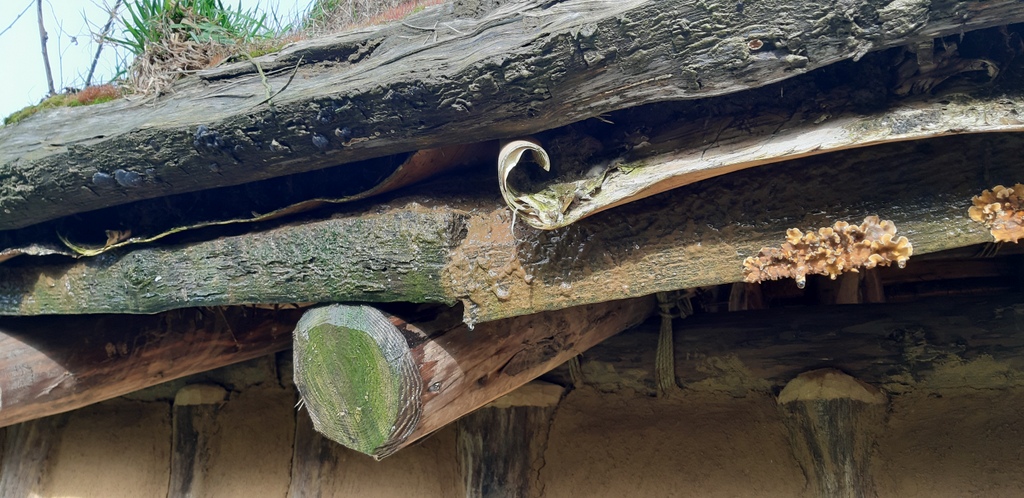


Roof covering
Material(s): Sods
Manufacturing techniques: Cut out the grass sods in the immediate vicinity of the house; lay under the grass sods a layer of birch bark
Dimensions: Height : 4000 mm | Width : 12500 mm | Depth: 5500 mm
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The grass sods have to be checked and repaired every year

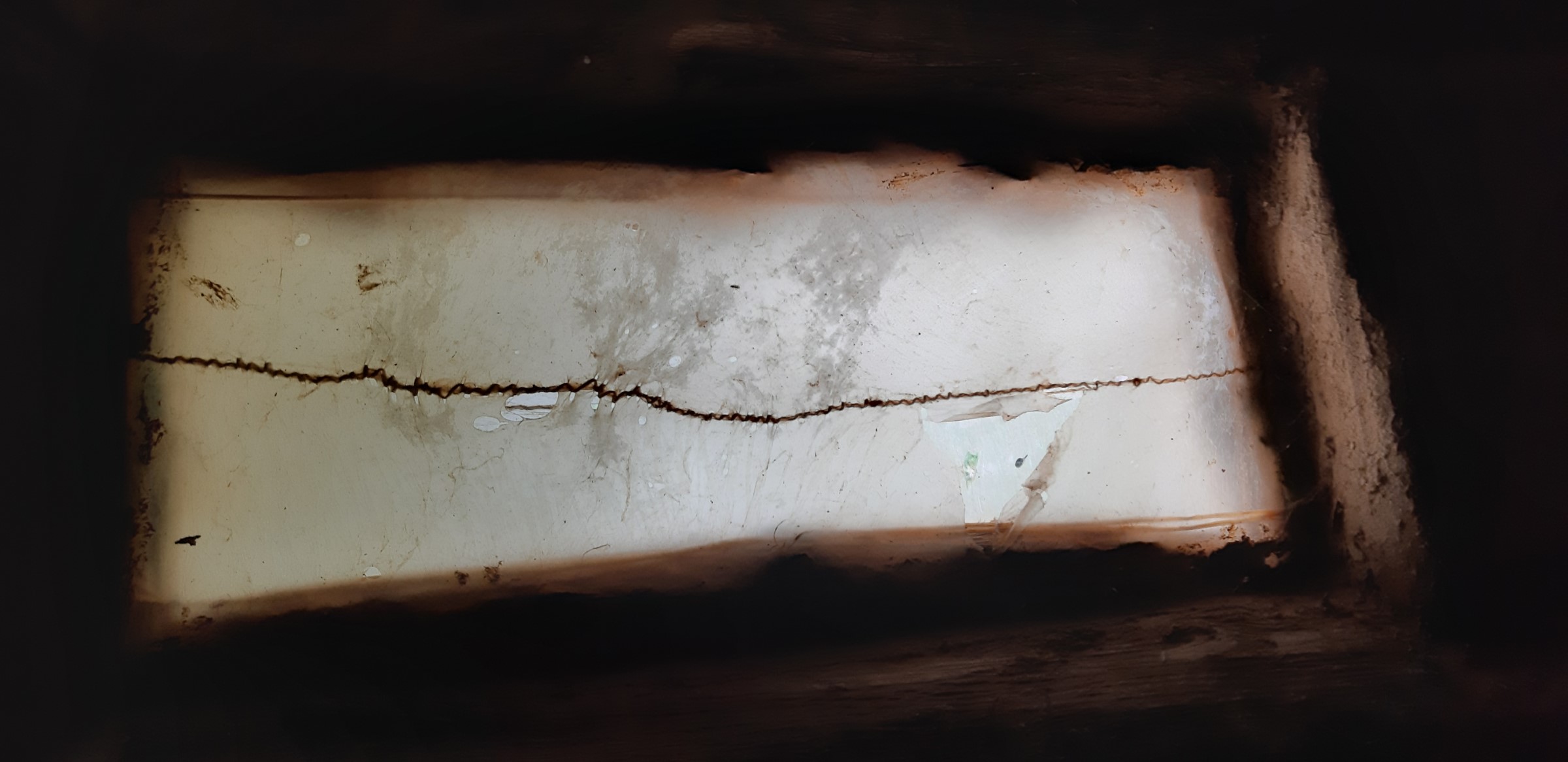
Are there windows in the building? Yes
Number of windows: 1
Window 1
In which room / where in the building is this window?
In room 2 (in the living room)
Describe the position in the room:
On the south side of the house, in ca. 1,5 m height
Dimensions: Height : 500 mm | Width : 300 mm | Depth: 5 mm
Type of window: Fixed window
Select material: leather - skin - parchment
Additional information about the selected material: Bovine bladder
Manufacturing technique:
To tan the skin / bladder first, dry it / as raw hide and fasten it on the window frame.
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The bladder / thin raw hide is very easily damaged.

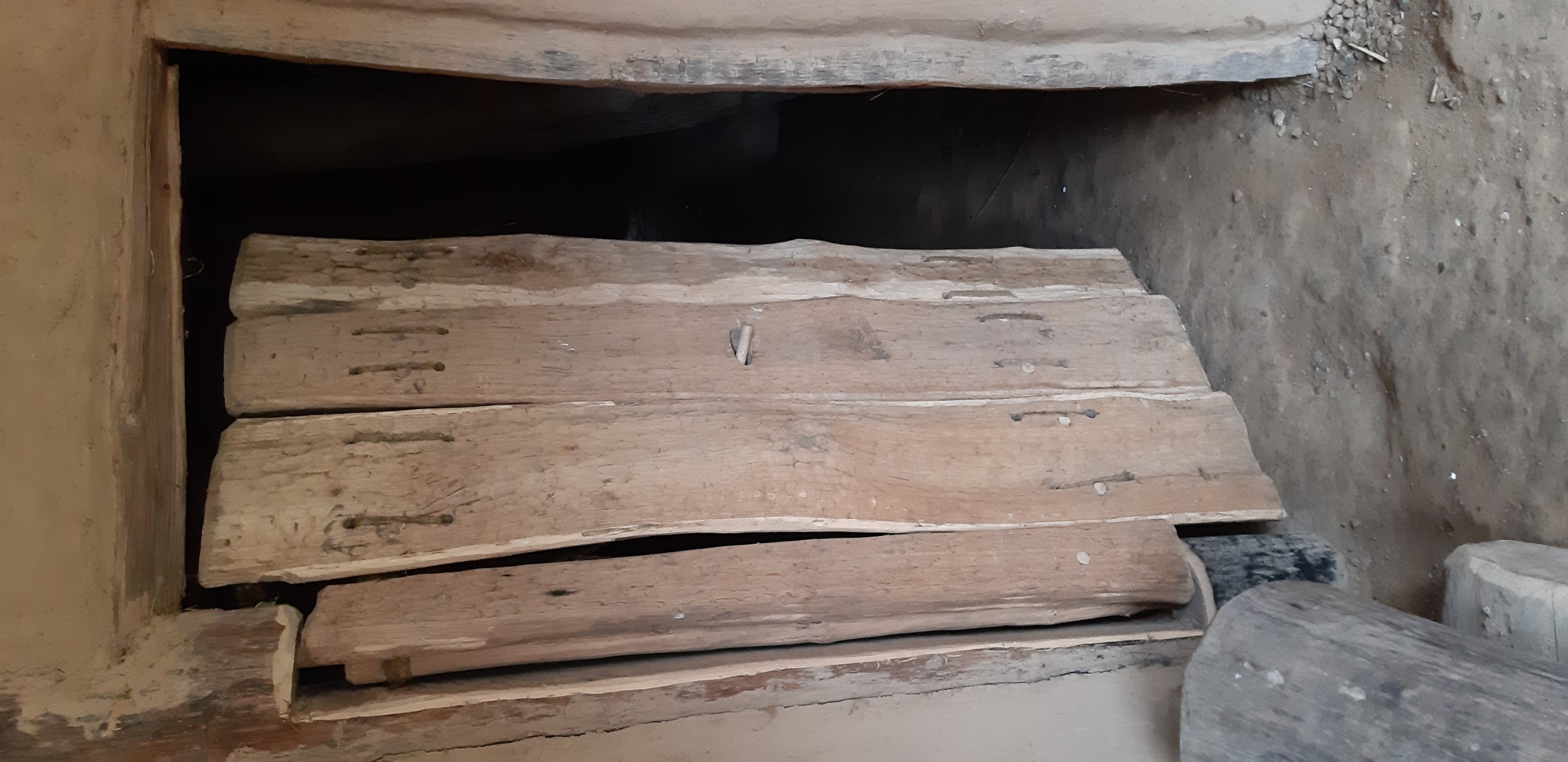
Are there doors in the building? Yes
Number of doors: 1
Door 1
In which room / where in the building is this door?
At the entrance to room 2 (from room 1)
Describe the position in the room:
On the edge of the short wall side
The door has: 1 leaf
Dimensions: Height : 2000 mm | Width : 1500 mm | Depth: 100 mm
Type of door: Ledged door
Select material: timber - wood
Additional information about the selected material: Oak wood
Manufacturing technique:
To prepare the wooden planks before
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The connecting parts of the door to the frame are very fragile and have to be checked regularly.

Are there stairs in the building? No
Are there wells in the building or attached? No
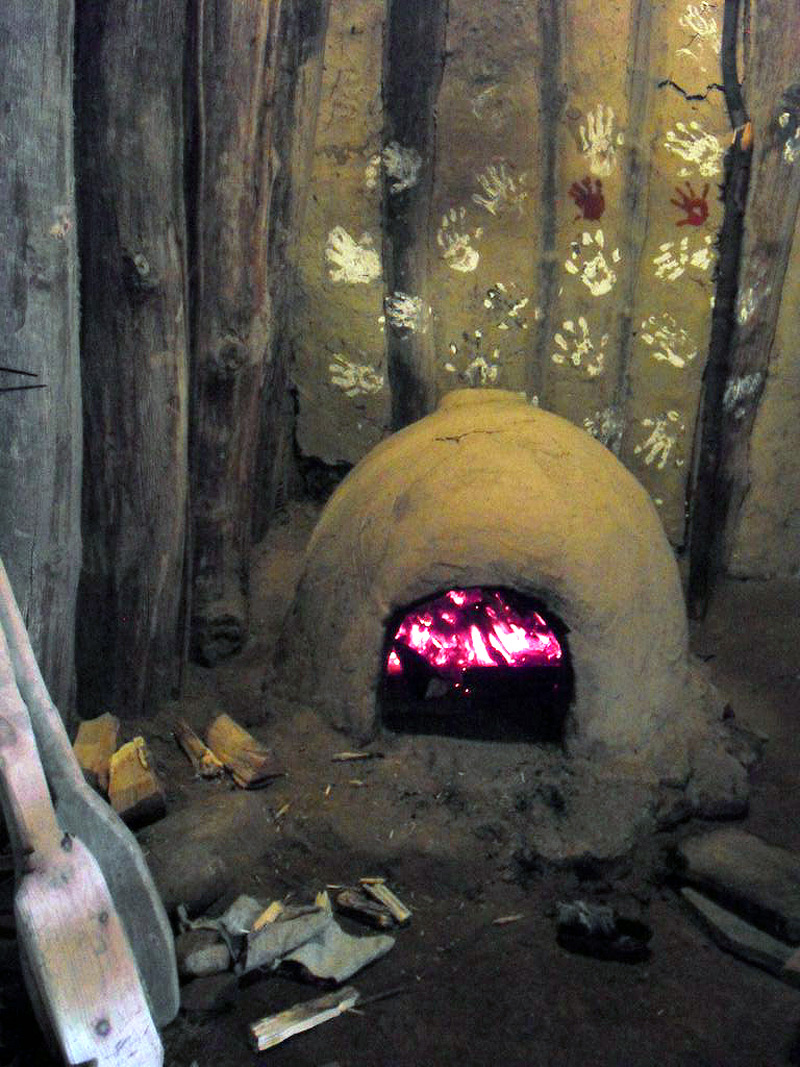
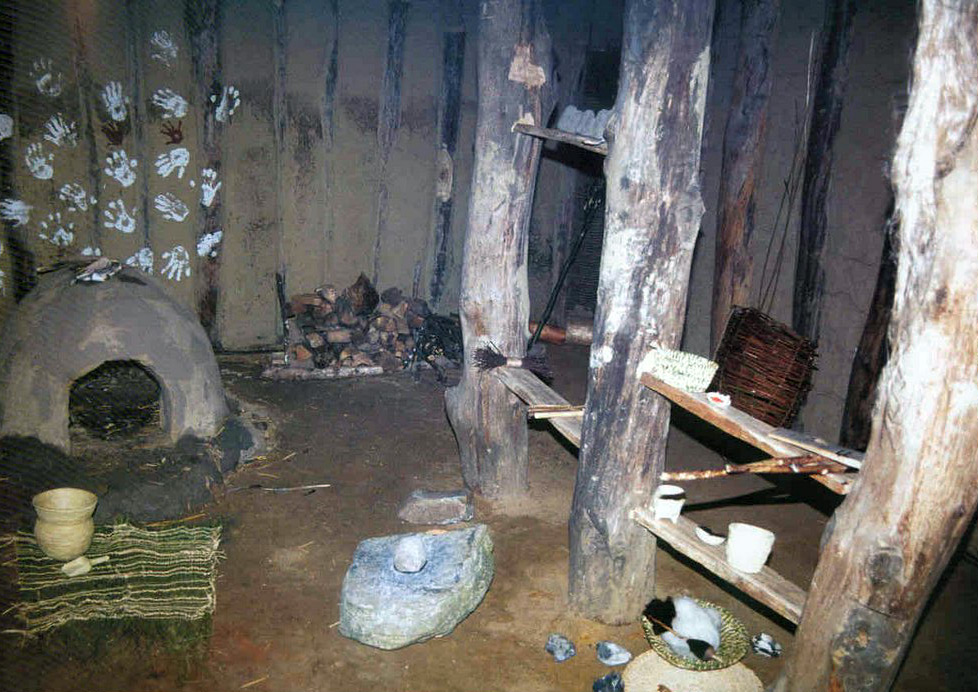
Are there fireplaces in the building? Yes
Number of fireplaces: 1
Fireplace 1
In which room / where in the building is this fireplace?
In room 2 / living room
Describe the position in the room:
Ton the wall
Dimensions: Height : 1000 mm | Width : 800 mm | Depth: 700 mm
Type of fireplace: Oven
Select material: mud - clay - sand
Additional information about the selected material:
Tempered clay (with sand, straw and cow dung)
Manufacturing technique:
Constructed by hand
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The clay surface has to be renewed after every third use

Is there smoke exhaust system in the building? Yes
Number of smoke exhaust systems: 1
Smoke exhaust system 1
In which room / where in the building is this smoke exhaust system?
Room 1, 2 and 3 / on the top of the wall just below the roof
Describe the position in the room:
On the top of the wall
Dimensions: Height : 900 mm | Width : 1000 mm | Depth: 100 mm
Type of smoke exhaust system: Smoke hole
Select material: timber - wood
Manufacturing technique:
Open the wattle and clay wall structure to deduct the smoke

Are there chimneys in the building? No
Please describe lighting system:
The lighting system are only the oven and oil lamps.
Are there decorative elements in the building? No
Number of decorative elements: 1
Decorative element 1
In which room / where in the building is this window?
In room 2 and 3 (living room and storage)
Describe the position in the room:
On the walls / on the clay surface
Type of decorative element: hands in colour
Material: pigments (f. e. charcoal or chalk)
Manufacturing technique:
Made by (coloured) hands
Describe the condition, decay, and parasites:
The decoration has to be renewed every year.

Are there inscriptions in the building? No